CNC processing is revolutionizing manufacturing. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the CNC machining market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on automation and precision in production processes. Industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics are leading the charge. Companies seek faster production times and reduced costs, which CNC processing provides.
CNC stands for computer numerical control. This technology uses computer software to manage machinery. Machines are programmed to cut, mill, or shape materials. This process ensures high precision and consistency. However, dependence on software can lead to challenges. Errors in programming can cause costly mistakes. It's crucial for operators to understand both hardware and software to succeed.
The potential of CNC processing is immense. The accuracy it offers translates directly into improved product quality. Yet, not all businesses have adopted this technology. Smaller companies may struggle with the initial investment costs. They must weigh the risks against the long-term benefits. As the industry evolves, these challenges highlight the need for continual adaptation and learning.

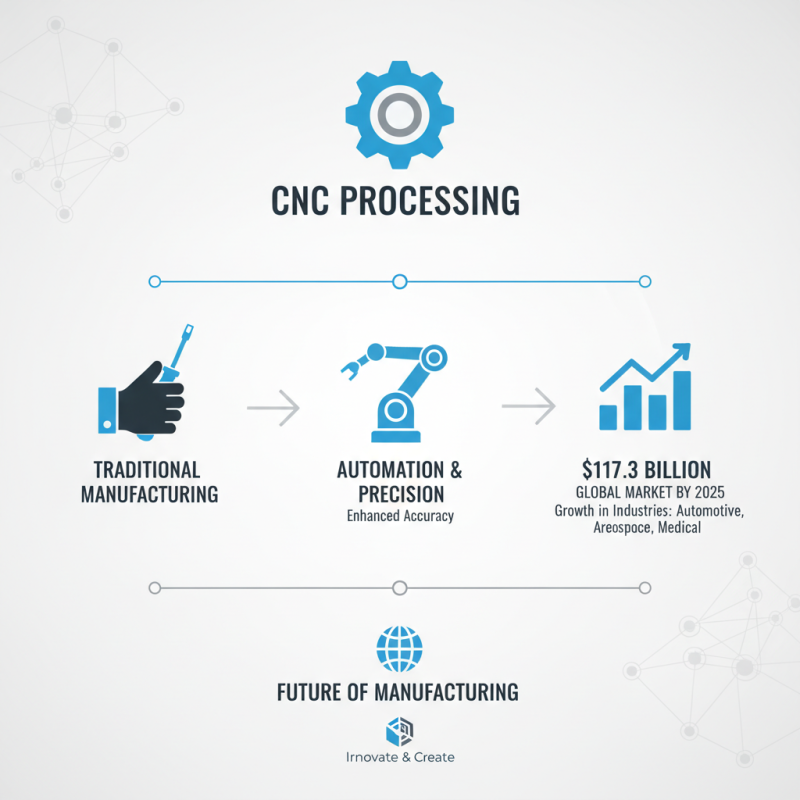
CNC processing, or Computer Numerical Control processing, is revolutionizing manufacturing. This technology automates machine tools and enhances precision. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global CNC machine market is projected to reach $117.3 billion by 2025. This growth emphasizes the increasing reliance on CNC in various industries.
CNC processing operates by translating digital designs into physical objects. A computer controls tools like lathes and mills, ensuring high accuracy. For instance, tolerances can be as tight as ±0.005 inches. However, not all CNC machines perform at the same level. Maintenance and calibration are crucial. A poorly calibrated machine can lead to wasted materials and time.
Moreover, skilled operators are essential. The automation of CNC does not eliminate the need for human supervision. Training is often lacking, leading to mistakes. Many companies overlook this aspect. A survey indicated that 30% of manufacturers reported skills gap issues affecting productivity. Addressing this gap is crucial for maximizing the benefits of CNC processing.
CNC technology has come a long way since its inception. Initially, it began as a mechanical endeavor using punched tapes and simple control units. This rudimentary setup limited the complexity of shapes and designs possible in manufacturing. Over time, machines became more sophisticated, integrating feedback loops and advanced algorithms. The rise of computer systems allowed for better precision and creativity.
The evolution continued with the advent of digital technology. Now, CAD software can create intricate designs. These designs are easily transformed into machine instructions. CNC machines became user-friendly, empowering even small businesses to adopt advanced manufacturing techniques. However, the rapid evolution also raises questions. Are operators skillful enough to handle these sophisticated machines? Relying too heavily on technology sometimes leads to a loss of hands-on skills in the workforce.
Today, CNC processing is ubiquitous in various industries. Yet, it is crucial to reflect on how automation changes job roles. As CNC systems grow more intelligent, the need for human oversight remains vital. Finding the balance between technology and skill is an ongoing challenge in this constantly evolving landscape.
CNC processing is a crucial element in modern manufacturing. CNC machines operate through a well-defined multi-step process. Initially, software creates a digital design, often using CAD. Once the design is ready, it’s converted into a CNC program, which translates the design into machine language. Reports suggest that approximately 70% of manufacturers rely on CNC technology for precision and efficiency.
The CNC machine uses motors and drives to control tool movement. It can manipulate materials with high accuracy, often down to one thousandth of an inch. These machines follow specific paths set by the program. However, even advanced systems can face challenges. For instance, calibration errors can occur, causing deviations in production. A survey indicated that 30% of CNC operators reported inconsistencies during production runs.
During machining, the cutting tool engages with the material. This removal process is efficient but not without risk. Overheating can lead to tool wear or even part failure. Operators must monitor operations closely to mitigate these issues. Reports show that improper setup can result in costly scrap rates, sometimes exceeding 5% of total production. This highlights the need for continuous training and assessment in CNC operations.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are crucial in modern manufacturing. They come in various types, each serving unique applications. The primary types include CNC mills, lathes, plasma cutters, and laser cutters. According to a recent industry report, the CNC machining market is expected to reach $100 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the rising demand across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
CNC mills are widely used for milling operations. They can create complex shapes and precise parts. Lathes, on the other hand, excel in turning operations. They produce cylindrical parts effectively. Plasma and laser cutters are vital for cutting materials like metal and plastic. Each machine type requires specific programming and skills. A significant challenge lies in the need for trained operators who can maximize machine capabilities.
However, not all CNC machining processes are perfect. Some operators struggle with programming complexities. Data from the National Institute for Metalworking Skills indicates a skills gap in the workforce. This gap impacts productivity and quality. Continuous training is essential. Industry experts emphasize the importance of adapting to new technologies. As CNC machines evolve, so must the skills of those who operate them.
CNC processing offers several benefits that make it popular in manufacturing. One key advantage is precision. According to a report by the International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, CNC machines can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.01 mm. This level of accuracy is crucial for industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing. CNC technology significantly reduces human error, ensuring consistent quality across production runs.
However, there are limitations to consider. The initial investment for CNC equipment can be substantial, often ranging from tens of thousands to millions of dollars. Smaller businesses might struggle to justify these costs. Additionally, CNC programming requires skilled personnel, which can pose a challenge. Many companies report a skills gap in the workforce, limiting their ability to fully leverage CNC technology. Furthermore, while CNC machines can handle complex shapes, they may not be the best option for every project. For example, projects with very low volume might not benefit from CNC's efficiencies. This necessitates a careful evaluation of the technology's suitability for specific production needs.