In 2026, mastering metal stamping techniques becomes essential for manufacturers. The global metal stamping market is projected to reach $210 billion. This growth reflects the increasing demand for precision and efficiency in production processes. Companies need to adopt innovative methods to stay competitive.
Metal stamping offers various advantages, including cost-effectiveness and versatility. It enhances production speed and reduces material waste. However, many firms struggle to keep up with technological advancements. They often rely on outdated practices, which limits their potential. Continuous learning in metal stamping is critical for success.
As industries evolve, the challenges become apparent. Achieving precision in metal stamping requires a deep understanding of materials and machinery. Some businesses still overlook the importance of skilled technicians. Developing a workforce that can operate complex stamping machines is crucial. Embracing new technologies while refining existing skills will define leaders in the field. An ongoing commitment to education will be key for those seeking to excel in metal stamping in 2026.

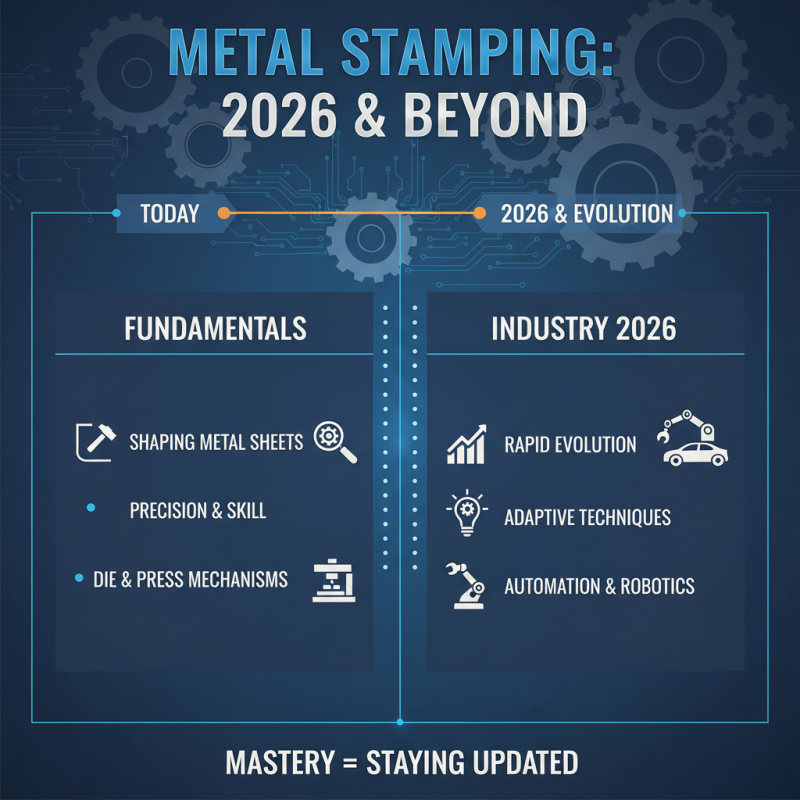
Metal stamping is a crucial technique in manufacturing. Understanding its fundamentals is essential for mastery. In 2026, industries are evolving rapidly. Staying updated on these techniques is vital. Metal stamping involves shaping metal sheets into desired forms. This process requires precision and skill.
The machinery used in metal stamping varies widely. It ranges from simple manual tools to advanced automated systems. Each tool offers unique challenges and opportunities. Learning to operate these machines can be daunting. Many face difficulties in achieving consistent results. Sometimes, it’s the small adjustments that make a big difference.
Material selection is another critical aspect. Different metals respond differently to stamping. Understanding these properties can lead to better outcomes. However, trial and error is often part of this journey. Not every attempt will result in perfection, and that’s okay. Reflecting on failures can lead to invaluable insights. In the quest to master metal stamping, perseverance is key.
Metal stamping is a craft that requires precision and the right tools. To excel in this technique, understanding the key equipment is essential. A variety of presses, dies, and cutting tools play critical roles. For instance, a hydraulic press can deliver the force needed for shaping metal sheets. Meanwhile, custom dies ensure the accuracy of shapes produced.
Tips: Always check your machinery before starting a project. A well-maintained press works better and produces higher quality results.
Other important tools include shears for cutting and punches for detailed designs. A good workbench provides stability, which is crucial during complex tasks. Ensure your workspace is organized to minimize distractions. Poor organization can lead to mistakes in measurements.
Tips: Keep smaller tools in designated spots. This will save time and reduce frustration during busy sessions.
Using these tools effectively involves practice. Beginners may struggle with consistency. That’s normal. Take time to reflect on each project. Learn from minor errors. Adjust your technique as you go. Improvement comes with patience and perseverance.
Mastering metal stamping requires precision and practice. In 2026, the global metal stamping market is projected to reach $20 billion. This growth highlights the increased demand for skilled technicians. Understanding the processes is crucial for professionals in this evolving field.
To begin, familiarize yourself with essential tools like dies and presses. Each piece plays a role in the stamping process. For instance, using the wrong die can compromise the quality of the finished product. Pay attention to the material properties. Certain metals respond better to stamping, while others can fracture or deform.
Practice makes perfect. Regularly experiment with different techniques. Track your progress and reflect on failures. Each setback offers a lesson. Engaging in workshops or online courses can provide valuable insights. According to recent industry reports, 30% of metal stamping failures occur due to a lack of training. Continuous learning is key to avoiding such pitfalls.
Quality control in metal stamping is crucial for ensuring the integrity of finished products. Research indicates that nearly 20% of production defects arise from inadequate quality checks in the stamping process. A robust quality control system can significantly reduce these issues. Regular inspections during production can detect flaws early, minimizing waste and cost.
Implementing a structured approach to quality control consists of three main practices. First, conduct thorough material inspections. This step ensures that the metal used meets the required specifications. Next, use statistical process control (SPC) to monitor every stage of production. SPC helps identify trends and deviations in real-time. Lastly, consider post-production audits for finished parts. These audits help verify that the final output aligns with design specifications.
A common challenge is the reliance on visual inspections alone. While visual assessments are necessary, they often overlook subtle defects. Additionally, operators may miss issues due to fatigue or distraction. This highlights the need for a combination of automated systems and human oversight. By blending technology with traditional methods, companies can enhance quality and reliability and create a culture of continuous improvement.
In 2026, the metal stamping industry is undergoing significant changes. New technologies are changing how manufacturers work. Automation and AI are increasingly popular. These innovations enhance precision and speed. However, they also demand skilled workers who can adapt quickly.
One emerging trend is the use of smart machinery. These machines can analyze data in real-time. They improve production efficiency. Yet, not all manufacturers have embraced this technology. Some struggle with the initial investment. Adapting to these systems can be slow. This creates gaps in productivity.
**Tip:** Invest time in training your team. Understanding new technology is vital. Offer regular workshops and encourage questions. Another consideration is sustainability. Eco-friendly stamping techniques are gaining traction. Yet, transitioning to greener options can be difficult for some. Balancing cost and sustainability is challenging.
**Tip:** Research local materials for eco-friendliness. This can lower costs and enhance your brand image. Staying updated with trends is crucial. Follow industry forums and attend workshops. These steps can help navigate challenges and embrace innovation.
| Technique | Description | Emerging Trend | Innovation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progressive Stamping | A method where multiple stamping operations are performed in a single machine. | Increased automation for efficiency. | Integration of advanced robotics. |
| Metal Forming Simulation | Utilizing software to predict the outcomes of metal forming processes. | Greater reliance on simulation software. | Real-time simulations for immediate adjustments. |
| Hybrid Metal Stamping | Combining traditional methods with 3D printing technologies. | Rapid prototyping capabilities. | 3D printed dies for complex geometries. |
| Servo Press Technology | Using servo motors for enhanced precision and control in stamping. | Higher flexibility in production runs. | Smart sensors for real-time monitoring. |
| Eco-Friendly Stamping | Techniques that reduce waste and energy usage. | Sustainable materials and processes. | Use of biodegradable lubricants. |